Understanding the Role of Health Savings Accounts with Insurance
Health care costs can be daunting, and with the right strategies, you can better manage these expenses. One such strategy is using a Health Savings Account (HSA) in conjunction with your health insurance plan. An HSA can offer a valuable financial cushion for medical expenses, but understanding its role and how it complements your insurance is crucial. This article will explore what HSAs are, how they work with insurance, and the benefits they provide.
What Is a Health Savings Account (HSA)?
A Health Savings Account is a tax-advantaged savings account designed specifically for individuals with high-deductible health plans (HDHPs). HSAs allow you to save money for qualified medical expenses, giving you a way to pay for health care while enjoying tax benefits. Here’s a closer look at how HSAs work:
- Eligibility: To open an HSA, you must be enrolled in a qualified HDHP, which generally has higher deductibles and lower premiums than traditional health plans. For 2024, the IRS defines HDHPs as having a minimum deductible of $1,600 for individual coverage and $3,200 for family coverage.
- Contributions: You can contribute to your HSA on a pre-tax basis, reducing your taxable income. For 2024, individuals can contribute up to $3,850, while families can contribute up to $7,750. If you’re 55 or older, you can make an additional catch-up contribution of $1,000.
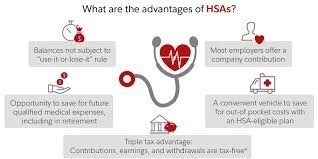
- Tax Advantages: Contributions to HSAs are tax-deductible, growth on your investments within the account is tax-free, and withdrawals for qualified medical expenses are also tax-free. This triple tax advantage makes HSAs an attractive savings tool.
How HSAs Work with Health Insurance
Health Savings Accounts are designed to work in tandem with high-deductible health plans. Here’s how the integration of HSAs and insurance works:
1. Funding Your HSA
When you enroll in an HDHP, you can set up an HSA through your employer or a financial institution. Contributions can be made by you, your employer, or both. The money in your HSA can be used to pay for out-of-pocket medical expenses, such as:
- Deductibles: The amount you pay for covered health care services before your insurance plan starts to pay.
- Copayments: Fixed amounts you pay for specific services, such as doctor visits or prescriptions.
- Qualified Expenses: Other eligible expenses include dental work, vision care, and some over-the-counter medications.
2. Paying for Medical Expenses
Using your HSA funds to pay for qualified medical expenses can help you manage out-of-pocket costs more effectively. For instance, if you have a $3,000 deductible and an HSA with $1,500 saved, you can use that amount to cover a portion of your deductible. This way, you minimize the impact of the deductible on your budget.
3. Investing HSA Funds
Another appealing aspect of HSAs is the ability to invest your contributions in various financial instruments, such as stocks and mutual funds. This can allow your savings to grow over time, providing a larger financial cushion for future medical expenses. However, keep in mind that investment options may vary based on the HSA provider.
Benefits of Health Savings Accounts
HSAs offer numerous benefits that can enhance your overall health care strategy:
1. Financial Flexibility
Having an HSA gives you flexibility in managing medical expenses. You can decide when and how to use your funds based on your health care needs, making it easier to budget for unexpected costs.
2. Long-Term Savings Potential
Because HSA funds roll over from year to year and don’t expire, you can build a substantial nest egg over time. This can be particularly beneficial as you approach retirement, where medical expenses often increase.
3. Retirement Health Care Planning
HSAs can also serve as a supplementary retirement savings vehicle. Once you turn 65, you can withdraw funds for any purpose without penalty—though you will pay income tax if not used for qualified medical expenses. This feature provides additional financial security during retirement.
4. Tax Benefits
The triple tax advantage of HSAs—tax-deductible contributions, tax-free growth, and tax-free withdrawals for qualified expenses—can help you maximize your health care budget. This advantage can be especially beneficial for those in higher tax brackets.
Considerations When Using an HSA
While HSAs are beneficial, there are a few considerations to keep in mind:
1. High-Deductible Requirement
To qualify for an HSA, you must be enrolled in a high-deductible health plan. This may not be suitable for everyone, especially those who prefer lower out-of-pocket costs.
2. Contribution Limits
Annual contribution limits can restrict how much you can save in your HSA. Ensure you’re aware of these limits and plan accordingly to maximize your savings potential.
3. Qualified Expenses
It’s essential to understand what constitutes a qualified medical expense. Using HSA funds for non-qualified expenses incurs a penalty, and understanding these rules is crucial to avoid costly mistakes.
Conclusion
Health Savings Accounts can play a pivotal role in managing your health care costs when used alongside high-deductible health plans. By providing a tax-advantaged way to save for medical expenses, HSAs enhance your financial flexibility and security. Understanding how HSAs work with your insurance can help you make informed decisions, ensuring that you’re prepared for any health care needs that arise.
With the right approach to HSAs and insurance, you can optimize your health care spending and protect your financial future.






Leave a Comment